Ensuring Network Resilience: The Importance of Redundancy in Fiber Network Design
For 2025, the reliability of fiber networks is paramount. That cannot be understated. Downtime can lead to significant financial losses, disrupted services, and a tarnished reputation. This is where redundancy in fiber network design comes into play. By incorporating redundancy and failover mechanisms, organizations can ensure network resilience and high availability, minimizing the risk of outages and maintaining seamless operations.
The Importance of Redundancy in Fiber Networks
Redundancy involves creating multiple pathways for data to travel within a network. This ensures that if one path fails, another can take over, maintaining the flow of data without interruption. The key benefits of redundancy include:
Increased Reliability: Redundant systems provide backup options, reducing the likelihood of complete network failure.
Enhanced Performance: By distributing traffic across multiple paths, redundancy can improve network performance and reduce congestion.
Business Continuity: Redundancy ensures that critical services remain operational even in the event of a failure, supporting uninterrupted business operations.
Risk Mitigation: Redundant systems help mitigate risks associated with hardware failures, cyber-attacks, and other unforeseen events.
Resource: Integrating and Future-Proofing Fiber Optic Networks
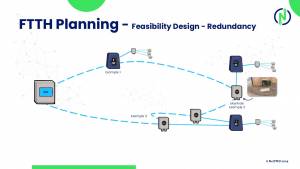
Implementing Redundancy in Fiber Networks: Key Protocols and Mechanisms
To achieve effective redundancy, several protocols and mechanisms can be employed. Here, we explore three key technologies: HSRP, VRRP, and MPLS.
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
HSRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol designed to provide high network availability by configuring multiple routers into a standby group. One router is designated as the active router, while another acts as a standby. If the active router fails, the standby router takes over, ensuring continuous network availability.
How It Works: HSRP creates a virtual IP address shared among the routers in the group. The active router handles traffic, while the standby router monitors its status. If the active router becomes unavailable, the standby router assumes the virtual IP address and takes over traffic forwarding.
Benefits: HSRP provides seamless failover, minimal downtime, and improved network reliability.
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
VRRP is an open standard protocol similar to HSRP, designed to increase the availability of the default gateway servicing hosts on a subnet. It allows multiple routers to work together to present the illusion of a single virtual router to the hosts.
How It Works: VRRP assigns a virtual IP address to a group of routers. One router is elected as the master, while others act as backups. If the master router fails, a backup router is elected to take over, ensuring uninterrupted network service.
Benefits: VRRP offers high availability, interoperability between different vendors’ equipment, and automatic failover.
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
MPLS is a versatile, high-performance technology that directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses. It is widely used for its ability to create efficient, scalable, and manageable networks.
How It Works: MPLS assigns labels to data packets, which are used to make forwarding decisions. This allows for the creation of predetermined, highly efficient paths through the network. MPLS can also support traffic engineering and VPNs, enhancing network flexibility and performance.
Benefits: MPLS provides improved network efficiency, reduced latency, and enhanced support for Quality of Service (QoS) and traffic engineering.
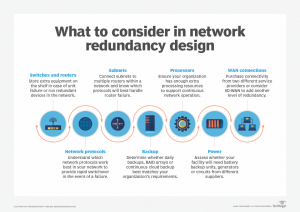
Source: TechTarget
Incorporating redundancy and failover mechanisms into fiber network design is essential for ensuring network resilience and high availability. By leveraging protocols like HSRP, VRRP, and MPLS, organizations can create robust, reliable networks that withstand failures and maintain continuous operations. As technology continues to evolve, staying ahead with effective redundancy strategies will be crucial for sustaining business continuity and delivering exceptional service.
Want to know how NetPMD can help you with your passive and active network design to ensure redundancy and network reliability is carefully considered? Then get in touch with our team today.




